本地或远程管理和控制Digi联网设备
管理联网的设备,首先是用Digi Remote Manager,通过它也可以实现私网的路由器管理。许多用户仍执着于本地接口的监控和管理,这虽然有一定意义,但如果是SIM卡发卡方的原因或是物理因素,这最多也只是记录log的手段而已。
虽然Digi可以提供方式,让SIM卡未正常连上网络时有了调试手段,但在阅读本文之前,请先了解:
1、Digi和北美欧洲运营商有全面的合作关系,您也可以通过Digi来获取北美或欧洲运营商的SIM卡,通过这种方式可避免因开卡问题引发的部署联网问题。
2、Digi有集中管理平台包括Digi Remote Manager设备云和On-Prem Manager本地管理软件,它们都可以支持私网SIM卡的管理,并且对IT管理非常友好,同时,DRM还支持通过API查询运营商的SIM卡状态和消费的流量信息
3、Digi路由器也支持SNMP软件来管理和配置SIM卡
4、Digi路由器支持通过ssh连接和执行相关的命令行,查询和设置SIM卡的连网情况,本功能可通过python或Java来实现程序接口而非交互式访问。
5、Digi的本地Web接口可对接口部分进行配置和查询
上面详述了Digi的路由器功能,通常出海企业最优的选择是通过Digi Remote Manager来远程管理设备,这也是最方便,最安全,功能最全的方式。
通过Digi Remote Manager的API获取LTE连网信息
虽然可以通过平台可视化地获取或配置相关信息,但如果是程序或自建管理平台需要的话,可以用API方式来实现相关的功能。
登陆到Digi Remote Manager后,点击右上角的配置齿轮图标,打开经典配置界面,然后点Documentation>API Explorer,在这里,您可以测试API功能,并导出相关例程,包括Java的支持。
点击SCI Target,从下拉窗口中添加您要测试的在线设备,然后在Example里选择v1/reports/devices/carrier,点击Send(首次使用会要求输入用户名和密码),就会向你的设备通过DRM发起一次Web请求,并返回相关的蜂窝网络连接信息。

点击Export,选择Java,就可以生成这个web service请求的例程,把它复制保存下来以备用:
注意,我们只需改变URL url = new URL(“https://remotemanager.digi.com/ws/v1/reports/devices/carrier”); 中的URL地址,就可以实现任意的http的请求。 同样的道理,选择请求类型为POST时,我们就获取到了相关的例程。
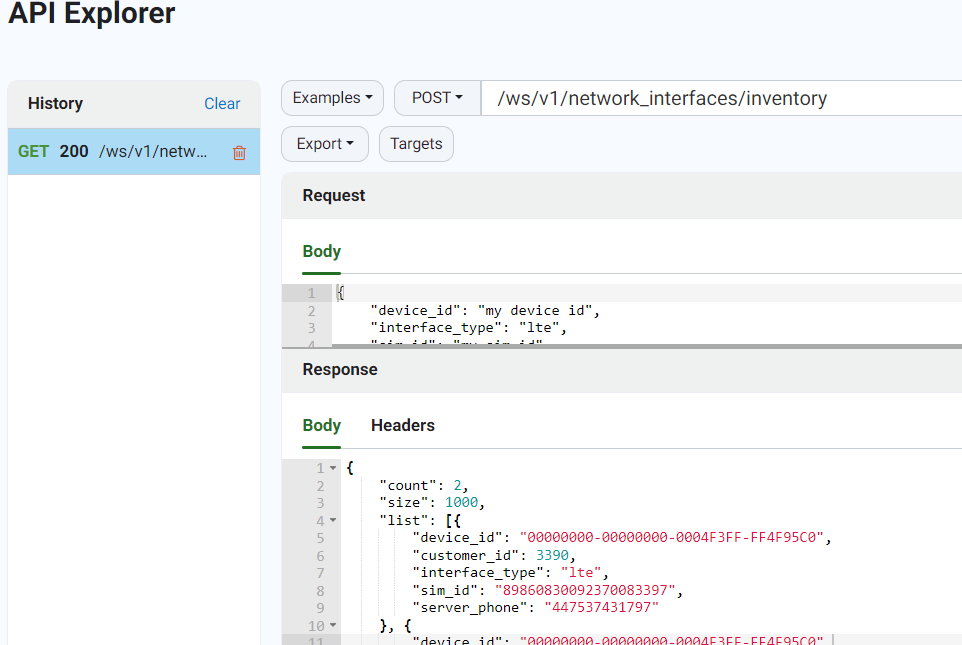
由于经典界面的例程不够多,下面我们回到当前DRM界面,在Example里选择V1/network_interfaces,发起post请求,便可以获取相关的SIM卡信息。
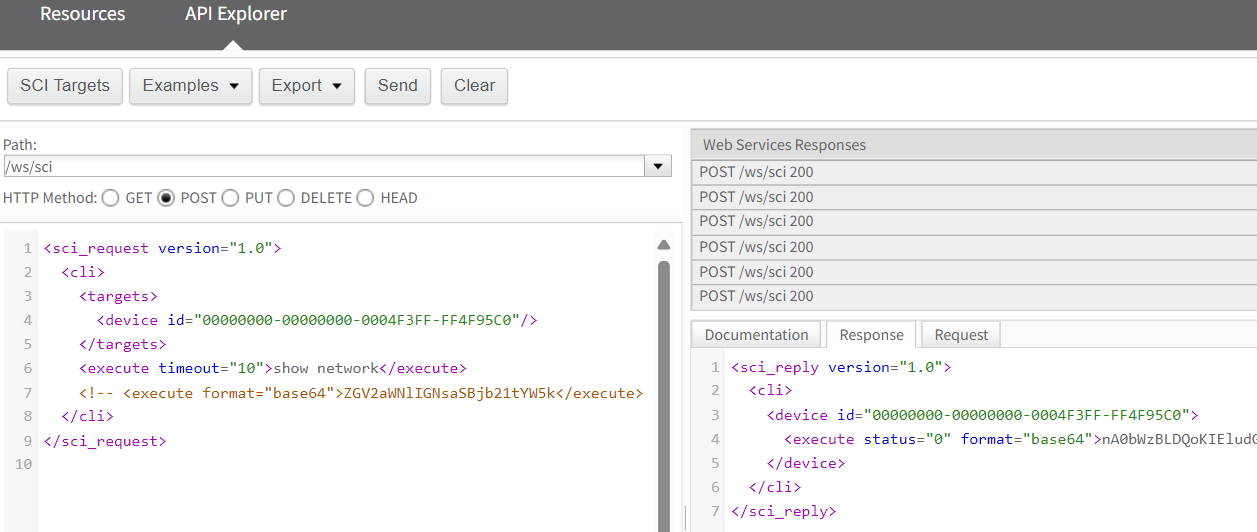
此外,在经典界面下,执行SCI>RCI的例程,也可从Query Device Setting或Status命令中获取更多有用的状态或配置信息。
用这种办法几乎可以获取路由器的任意信息,包括log的调试信息,因此非常方便。
通过本地REST接口或SNMP接口设置和获取相关信息
SNMP能实现大部分功能,包括读取SIM卡信息等,SNMP协议比较复杂,一般专业的网络管理软件支持SNMP协议来管理网络设备。详情请参考文档
REST API可以用于读取和设置部分信息,但并不支持读取Modem的相关配置,它的用法详见:使用本地基于Web的REST API 来配置DAL设备
要在本地使用完整功能,一般是可通过Python和Java来ssh到路由器设备并获取相关的CLI信息,这个方法和同DRM的API相比较为不方便,因为它不像DRM可以精细化的直接得到Json键值对,而是需要通过对seesion中命令的输出来提取相关信息。这里是一些示例,比如使用python或java来获取CLI的输出:

一、python的方式
确保你安装了paramiko库。如果你还没有安装,可以使用以下命令安装:
pip install paramiko
以下是
二、Java的实现方式
在Java中,你可以使用JSch库来实现SSH连接并执行命令,然后获取命令的执行结果。以下是一个简单的示例,演示如何使用JSch库来实现这一功能。
在这个代码示例中,sendCommand 方法用于发送命令到服务器,而 readOutput 方法用于读取命令的输出。请注意,你可能需要根据服务器的实际响应来调整 readOutput 方法中的结束标记,以便正确地捕获命令的输出。